Integrating ESG into Systems for Business Excellence: Empowering Indian Enterprises, from Large Corporations to Medium-Sized Firms
Introduction:
In an era marked by escalating environmental challenges, heightened social consciousness, and an imperative for robust corporate governance, the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into business operations has emerged as an indispensable facet of corporate prosperity. Projections indicate that ESG-aligned assets could surge to an astonishing $53 trillion by 2025, constituting a substantial share of global Assets Under Management (AUM), effectively reshaping investment landscapes. This transition within the investment community towards ESG considerations transcends conventional financial returns; it embodies a collective aspiration to foster a sustainable and just global ecosystem.
This comprehensive article delves into a pivotal juncture where the Baldrige Excellence Framework harmonizes with corporate strategies, offering a structured avenue for businesses to systematize ESG goals and ensure sustainability amidst an evolving landscape of regulatory shifts. By dissecting the enabler categories of the Baldrige Criteria, this article reveals how these organizational elements can be wielded as powerful instruments for aligning with ESG principles. This confluence not only paves the way for companies to thrive sustainably but also attracts investors.
Recent ESG Developments:
Europe’s ESG Mandates: Starting in January 2023, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) became effective in the European Union, necessitating social and environmental disclosure by large and listed companies. By July 2023, the European Commission introduced the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) for companies under CSRD jurisdiction, impacting reporting from the 2024 fiscal year.
Global Shift towards ESG Standards: On June 26, 2023, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) issued IFRS-S1 and IFRS-S2 standards for sustainability-related and climate-related financial disclosures. These standards, endorsed by the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO), stimulated global adoption and prompted public consultation in various countries for potential adoption.
India’s Commitment to ESG: On July 12, 2023, SEBI introduced regulations enhancing reporting and assurance of ESG practices for Indian companies. These regulations include:
– Starting from the 2023-24 financial year, the top 1000 listed entities are mandated to report using the revised Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) format.
– From 2023-24, the top 150 listed entities must undertake reasonable assurance of the BRSR Core.
– Beginning in 2024-25, the top 250 listed entities will disclose ESG practices across their value chain and obtain limited assurance from FY 2025–26.
How New ESG Regulations Impact Businesses:
Global ESG regulations, including those introduced by SEBI in India, and the alignment of global funds with ESG are set to create a value chain ripple effect. As companies adopt transparent reporting, they require verified data from their supplier and partners, setting off a ripple effect that spans industries and geographies. This means that to attract capital for their businesses, both large companies and MSMEs will need to showcase not only their returns on investment but also their ESG practices and sustainability impacts.
Integrating ESG into business systems, rather than treating it as a one-off requirement, is a strategic move. This approach ensures compliance with regulations and nurtures a culture of transparency, accountability, and sustainability within the organization’s system.
ESG and Baldrige Excellence Framework: A Confluence
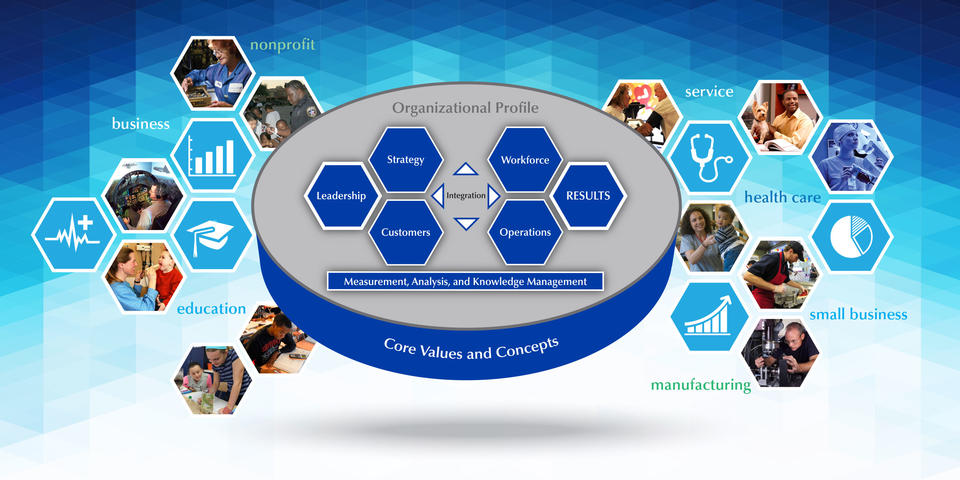
The confluence of ESG factors and the Baldrige Excellence Framework offers a unique approach to achieving ESG goals and ensuring sustainability. Baldrige Excellence Framework contains the Baldrige Criteria for Performance Excellence (Baldrige Criteria) and Core Values which are well accepted worldwide by companies for organizational performance improvement.
The seven categories of the Baldrige Criteria are usually seen in two groups: enablers and results categories. Out of a total of seven categories, the initial five, which include 1) Leadership, 2) Strategy, 3) Customers, 4) Measurement, Analysis, Knowledge Management, and 5) Workforce, are identified as Enablers. These Enablers provide a systematic approach for organizations to overall performance excellence which can cover ESG performance on set goals. Baldrige Criteria can not only help companies meet their ESG goals but also prepare them to navigate successfully and thrive in an increasingly ESG-conscious world.
ESG Focused Update in Baldrige Excellence Framework for 2023-24:
Incorporating the latest advancements in the business environment, the 2023–2024 updates to the Baldrige Excellence Framework (Baldrige Framework) shine a spotlight on crucial aspects that profoundly resonate with ESG topics of interest to investors. The updated Baldrige framework emphasizes key areas of focus:
a. Organizational Agility, Innovation, and Transformation: In an ever-evolving marketplace, the ability to adapt swiftly and continuously innovate is paramount. The Baldrige framework underscores the significance of agility, innovation, and transformation as drivers of success.
b. Risk Management and Supply-Chain Resilience: Recent global disruptions have underscored the importance of risk management and resilient supply chains. The Baldrige framework acknowledges these critical components of modern business resilience.
c. Societal Contributions and Environmental Sustainability: Beyond profitability, businesses today are expected to make meaningful societal contributions and demonstrate environmental responsibility. This framework encourages organizations to integrate these considerations into their core operations.
d. The Changing Nature of Work and Workforce Needs: The nature of work is undergoing rapid transformation, with remote work, automation, and evolving skill requirements. The Baldrige framework recognizes the need for businesses to adapt to these workforce changes.
e. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion: Inclusivity isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental aspect of contemporary business. The Baldrige framework places a strong emphasis on fostering diversity, equity, and inclusion within organizations.
Categories of Baldrige Criteraia and ESG Dimentions:
1. Category: Leadership
The Leadership category within the Baldrige Excellence Framework is the foundation upon which an organization’s success is built. It encompasses two critical subcategories: Senior Leadership and Governance and Social Contribution. Leadership is all about how an organization’s top executives steer the ship and how the organization fosters a sense of responsibility towards society. It asks tough questions about ethics, communication, accountability, and societal contributions.
1.1. Senior Leadership:
The first subcategory, Senior Leadership, delves into how the top brass of an organization sets the tone and direction. It’s not just about the C-suite; it’s about the values they uphold and how they communicate and implement them. It asks questions like how senior leaders deploy the organization’s mission, vision, and values. How do they promote legal and ethical behavior? How do they create an environment that values diversity, equity, and inclusion? Answering these questions not only demonstrates ethical leadership but also showcases a company’s commitment to governance, ethics, and social responsibility, which is at the core of ESG alignment.
1.2. Governance and Social Contribution:
The second subcategory, Governance and Social Contribution tackles the nuts and bolts of how an organization governs itself and contributes to society. It asks about accountability, fiscal transparency, stakeholder interests, and even succession planning. Moreover, it inquires about how the organization addresses legal and ethical behaviour, as well as how it incorporates societal well-being and benefits into its operations. By answering these questions effectively, a company can highlight its commitment to transparency, social responsibility, and ethical governance – all of which resonate strongly with ESG investors.
How it Showcases ESG Alignment:
Leadership, particularly senior leadership, sets the tone for an organization’s commitment to ESG. Through their actions and decisions, senior leaders demonstrate dedication to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. They lead by example when it comes to governance and social contribution, showing that ethical behaviour, transparency, and accountability are fundamental values. This aligns with the ESG dimension of “Corporate Governance.”
Furthermore, leadership’s commitment to creating a positive workforce environment and engaging with the workforce directly influences “Workforce” aspects of ESG, promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI). When senior leaders prioritize workforce engagement and retention, they contribute to human rights and community support, essential elements of the ESG framework.
2. Category: Strategy
Strategy is the compass that guides an organization’s journey, and the Baldrige Excellence Framework recognizes this with its Strategy category. It dissects how an organization develops and implements its strategy. This category is divided into two key subcategories: Strategy Development and Strategy Implementation. It probes into how an organization navigates its challenges and opportunities in a way that’s not just financially savvy but also ethically and environmentally responsible.
2.1. Strategy Development:
The first subcategory, Strategy Development, examines the process by which an organization identifies its strategic goals and plans. It involves anticipating future challenges, considering innovations and emerging technologies, and making decisions about core competencies and resources. Essentially, it asks how an organization aligns its strategic objectives with ESG priorities. Answering these questions demonstrates a company’s commitment to aligning its core strategies with environmental and societal concerns – a powerful message for ESG investors.
The second subcategory, Strategy Implementation, takes the strategic plan and puts it into action. It’s about translating intentions into results. It emphasizes resource allocation, workforce preparation, and adaptation to changing environments. Additionally, it highlights the agility and resilience of an organization. Addressing these questions effectively showcases a company’s ability to not only strategize but also to execute those strategies in a way that’s congruent with ESG goals.
How it Showcases ESG Alignment:
The development and implementation of strategy are critical for integrating ESG aspects into an organization. A well-crafted strategy that includes sustainability initiatives, clean energy transition, responsible resource management, and climate change mitigation aligns with the ESG dimension of “Environmental.” It showcases the company’s commitment to reducing its environmental footprint, addressing climate change challenges and seizing environmental opportunities.
Moreover, a strategy that prioritizes customer expectations and engagement contributes to the ESG aspect of “Customer Responsibility.” By actively involving customers in product development and incorporating their values, companies show that they consider customer well-being and preferences.
3. Category: Customers
The Customers category recognizes that a business exists to serve its customers. It explores how an organization listens to its customers, determines products and services to meet their needs, builds lasting relationships, and enhances the overall customer experience. This category includes two significant subcategories: Customer Expectations and Customer Engagement.
3.1. Customer Expectations:
The first subcategory, Customer Expectations, is all about understanding what customers want and need. It delves into how an organization listens to customers, whether they are existing, potential, or former. It also explores how an organization segments its customers and tailors its offerings to meet diverse customer expectations. This subcategory, in essence, asks how a company aligns its products and services with societal and environmental expectations.
3.2. Customer Engagement:
The second subcategory, Customer Engagement, focuses on how an organization builds and manages customer relationships. It includes elements like relationship management, accessibility, support, and complaint management. Crucially, it asks about fair treatment and how the organization ensures that its customer experience processes promote equity and inclusion for a diverse customer base. Addressing these questions effectively not only enhances customer engagement but also showcases a company’s commitment to social responsibility and ethical customer treatment.
How it Showcases ESG Alignment:
Understanding and meeting customer expectations is fundamental to ESG alignment. By actively seeking feedback, responding to customer concerns, and ensuring data privacy and security, companies demonstrate their commitment to the “Customer Responsibility” aspect of ESG. Engaging with customers to provide eco-friendly products or services showcases dedication to environmental sustainability, a key component of ESG.
Furthermore, strong customer engagement fosters loyalty and trust, which are vital for a company’s reputation in terms of governance and social contribution, aligning with ESG’s “Corporate Governance” and “Social Supply Chain” dimensions.
4. Category: Measurement, Analysis, and Knowledge Management
This category delves into the critical aspect of evaluating and improving organizational performance. It encompasses two subcategories: Measurement, Analysis, Review, and Improvement of Organizational Performance, and Information and Knowledge Management.
4.1. Measurement, Analysis, Review, and Improvement of Organizational Performance:
The first subcategory concentrates on how an organization tracks its performance, reviews its progress, and initiates improvements. It explores the use of performance measures and comparative data, ensuring that decision-making is based on facts. This subcategory plays a crucial role in showcasing ESG alignment, as it evaluates how well an organization is meeting its ESG-related goals.
4.2. Information and Knowledge Management:
The second subcategory deals with how an organization manages its data and knowledge assets. It focuses on data quality, availability, and cybersecurity. It also emphasizes the importance of organizational knowledge and the pursuit of innovation. Effective information and knowledge management are essential for demonstrating transparency, accountability, and responsible innovation – all integral components of ESG alignment.
How it Showcases ESG Alignment:
Robust measurement, analysis, and knowledge management processes are essential for tracking and improving ESG performance. By consistently measuring and analyzing environmental impacts, organizations align with the “Environmental” aspect of ESG. This data-driven approach enables companies to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate transparency in addressing environmental challenges.
Effective knowledge management also supports ESG alignment by ensuring that information related to ESG material issues is readily available to decision-makers. This aligns with the ESG dimension of “Information and Knowledge Management,” contributing to transparency and accountability.
5. Category: Workforce
Introduction:
The Workforce category recognizes that an organization’s people are its most valuable asset. It focuses on creating a workplace that supports high performance and engagement. This category includes two subcategories: Workforce Environment and Workforce Engagement.
5.1. Workforce Environment:
The first subcategory, Workforce Environment, is all about assessing and meeting the workforce’s capability and capacity needs. It encompasses hiring, onboarding, managing change, and addressing workplace health. It is crucial in showcasing a company’s commitment to fostering a diverse and inclusive workforce, which is a vital aspect of ESG alignment.
5.2. Workforce Engagement:
The second subcategory, Workforce Engagement, emphasizes the importance of engaging the workforce for retention and high performance. It involves assessing engagement drivers, ensuring equity and inclusion, and promoting learning and development. Addressing these questions effectively not only enhances workforce engagement but also showcases a company’s commitment to ESG principles, including diversity, equity, and inclusion.
How it Showcases ESG Alignment:
A company’s treatment of its workforce is a critical aspect of ESG. Creating a positive workforce environment, promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), and prioritizing workforce engagement all directly align with ESG principles.
A workforce environment that fosters DEI supports human rights and community engagement, vital components of the ESG framework. It showcases a commitment to treating all employees fairly and ensuring equal opportunities.
Furthermore, workforce engagement and retention demonstrate a company’s dedication to providing good jobs, ensuring job quality, and supporting labour standards, which are key dimensions of ESG. This aligns with ESG’s focus on social supply chain responsibility and workforce well-being.
By considering these dimensions of ESG in each category, organizations can effectively integrate ESG aspects and material issues into their systems for continual improvement and communication with stakeholders. This comprehensive approach not only strengthens their ESG offerings but also enhances their ability to showcase ESG alignment to investors and other stakeholders.
Conclusion:
In the pursuit of corporate excellence, the Baldrige Excellence Framework emerges as an invaluable ally for businesses, regardless of their scale, seeking to navigate the complex terrain of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. As the world ushers in an era where ESG considerations are no longer optional but imperative, the Baldrige framework offers not just a guide to excellence but a roadmap to lasting sustainability.
Incorporating ESG principles into every facet of business systems is no longer a choice; it’s a strategic imperative. By embracing the Baldrige Excellence Framework, organizations, from large corporations to medium-sized enterprises, can methodically integrate ESG into their DNA, ensuring not only compliance with regulations but the creation of a brighter, more sustainable future. This convergence of corporate excellence and ESG values not only enhances a company’s appeal to investors but also contributes significantly to the global quest for environmental responsibility, social equity, and ethical governance, forging a path towards a better world for all.